ICSR Process

ICSR Process
ICSR i.e. Individual Case Safety Report
ICSR Process is a part of the Pharmacovigilance Process.
Individual Case Safety Report (ICSR) refers to the format and content for the submission of an individual report of suspected adverse reactions in relation to a medicinal product that occur in a single patient at a specific point of time. (GVP Guidelines)
A valid ICSR should include an identifiable reporter, an identifiable patient, an adverse reaction, and a suspect medicinal product.
Who all are involves in ICSR Process?
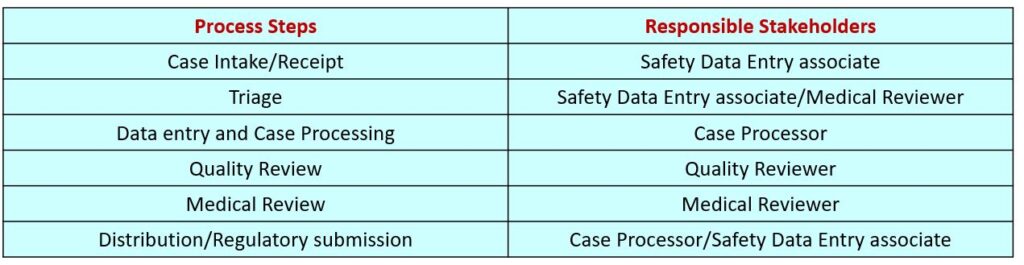
The following stakeholders involves in ICSR Process
- Safety Data Entry associate (SDEA)
- Case Processor (CP)
- Quality Reviewer (QR)
- Medical Reviewer (MR)
*Translator –To translate the local language Adverse events reports into English
ICSR stakeholders should considered the main principles while case processing
- Enter data as provided by the reporter
- No local language data should be translated to English
- No interpretation, assumptions, or judgment
Table of Contents
ICSR Process
The following steps involves in ICSR Process
- Case Intake/Receipt
- Triage
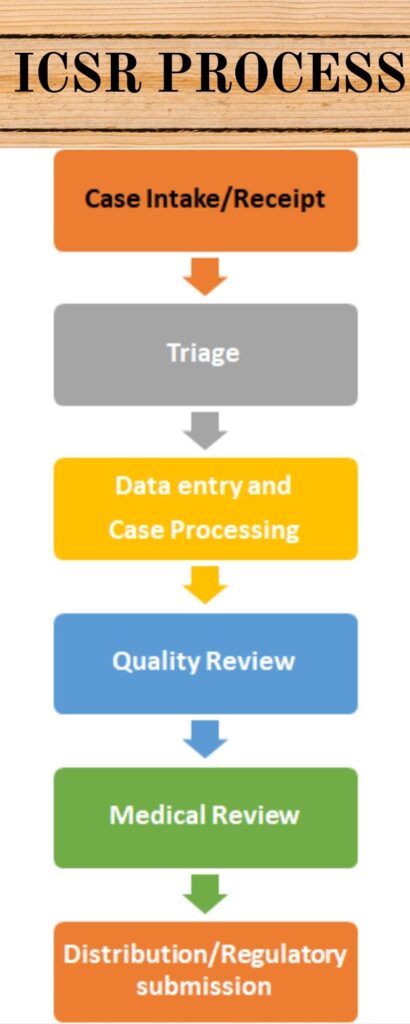
Individual Case Safety Report (ICSR) Process - Data entry and Case Processing
- Quality Review
- Medical Review
- Distribution/Regulatory submission
As we discussed in our previous post “Pharmacovigilance Process”: Every company maintains its own Pharmacovigilance safety database.
What is a safety database?
The Safety Data Base is the central repository of ICSR’s collected for a company’s drug(s) from all global sources.
It is critical that any safety database be maintained with the latest regulatory requirements and validated to
meet international standards and business requirements.
Here you can find some of the safety databases using in the industry
- Argus
- ARISg/LifeSphere Safety
- PV Works
- SafetyEasy
- SafetyBase Interchange
Note: For Good Pharmacovigilance Practice, safety databases should be compliant with 21 CFR part 11.
All activities and decisions taken throughout the ICSR process are documented within the safety database.
ICSR Process Step 1: Case Intake/Receipt
- Tools used for the receipt of source documents (Adverse event reports), such as email or fax
- SDEA monitors at a minimum once daily every business day
- SDEA receive reports in various formats, including but not limited to electronic or paper format
- Determining case validity – Only valid cases qualify for regulatory reporting
- Determine the case type (solicited and unsolicited report types)
- Translate adverse event reports of their country into English
- Request additional medical information where necessary
- SDEA performs duplicate check-in safety databases before the entry of an ICSR
- Database will be searched to investigate if the case is a new initial case (i.e., has not been entered into the database before) or if it relates to a case which has been previously received
ICSR Process Step 2: Triage
Triage means
- to review, assess and prioritize received safety information and
- to record the minimal information required
- to quickly and reliably establish the case priority regarding expedited reporting requirements
Triage applies to all reported Adverse Events, special situations, and Product Complaints associated with Adverse Events from both solicited and unsolicited report types
So, it helps prioritize ICSRs in the safety database and placing them in the correct regulatory reporting section for submission.
In triage, two different processes are involves,
- Triage of any newly received ICSR information and
- Secondly the medical assessment (Medical triage)
SDEA responsible for triage for a first preliminary assessment
- Determining case validity (valid or non-valid case)
- Assessment of seriousness for each adverse event
- Identification of suspect company product
- assessment of causality and listedness
- Case prioritization as per regulatory guidelines
Medical reviewer performs Medical triage
- All post-marketing cases (solicited and unsolicited) require a medical triage
- Complete assessment of seriousness for each adverse event
- Complete assessment of causality and listedness for each combination of suspect product and adverse event
- Assessment of whether the event is considered as an area of under monitoring
ICSR Process Step 3: Data entry and Case Processing
Case processor performs the below activities
- Determining case validity (valid or non-valid case)
- Duplicate check performs
- Enter sources of the case
- Data entry from adverse event report from into safety database
- Update Reporter and patient details in the safety database
- Enters medical history, and laboratory data as provided by the reporter
- Coding of medicinal products specified as suspect or concomitant by the reporter and update dosage, therapy dates, action taken for suspect products,
- Enters information about all reported reactions incl. MedDRA coding, start/stop dates,
- Adverse event data and coding using MedDRA
- Seriousness assessment
- Labelling and Causality assessment
- Assessment of dechallenge and rechallenge
- Event ranking in the safety database
- Narrative writing
- query creation to obtain additional information, case clarification, and additional details.
After data entry, the case processor route the case to the Quality review stage.
ICSR Process Step 4: Quality Review
- Quality reviewer perform quality analysis of the case to ensure accurate and consistent data entry and processing from adverse event reports
- Quality reviewer confirms case validity, event term selection and coding, coding of suspect products, and overall consistency of information.
- The quality reviewer also determines whether or not the follow-up information is medically significant.
- Quality reviewer assesses event listedness, evaluates/confirms the seriousness assessment, and completes or modifies the narrative as necessary
ICSR Process Step 5: Medical Review
- The activity Medical Review is performed by a safety physician (Medical reviewer)
- Physician review is the first-level step in signal detection activities
- Medical review checks the overall case assessment and the consistency of information including confirmation of listedness determination.
- The Medical reviewer performs the company causality assessment, company clinical evaluation comment, and completes the SUSAR process as appropriate.
- Medical reviewer has ultimate responsibility for seriousness assessment
- The case is checked from the medical perspective for completeness, correctness, and consistency
- MedDRA coding and narratives are reviewed from a medical perspective
- Check source data, if considered necessary based on medical judgment
- Medical reviewer provides Pharmacovigilance comment for all ICSRs except Spontaneous Non-Serious Listed ICSRs and Solicited Non-Serious Listed ICSRs
ICSR Process Step 6: Distribution/Regulatory submission
- After Medical review, cases are sent for distribution
- Distribution is nothing but submission of ICSR to Regulatory authorities
- Safety database is configured to allow automatic scheduling and generation of expedited and non-expedited reports
- Safety Data Entry associate responsible for monitoring the database worklist reports regularly to ensure appropriate and timely submissions
3 thoughts on “ICSR Process”